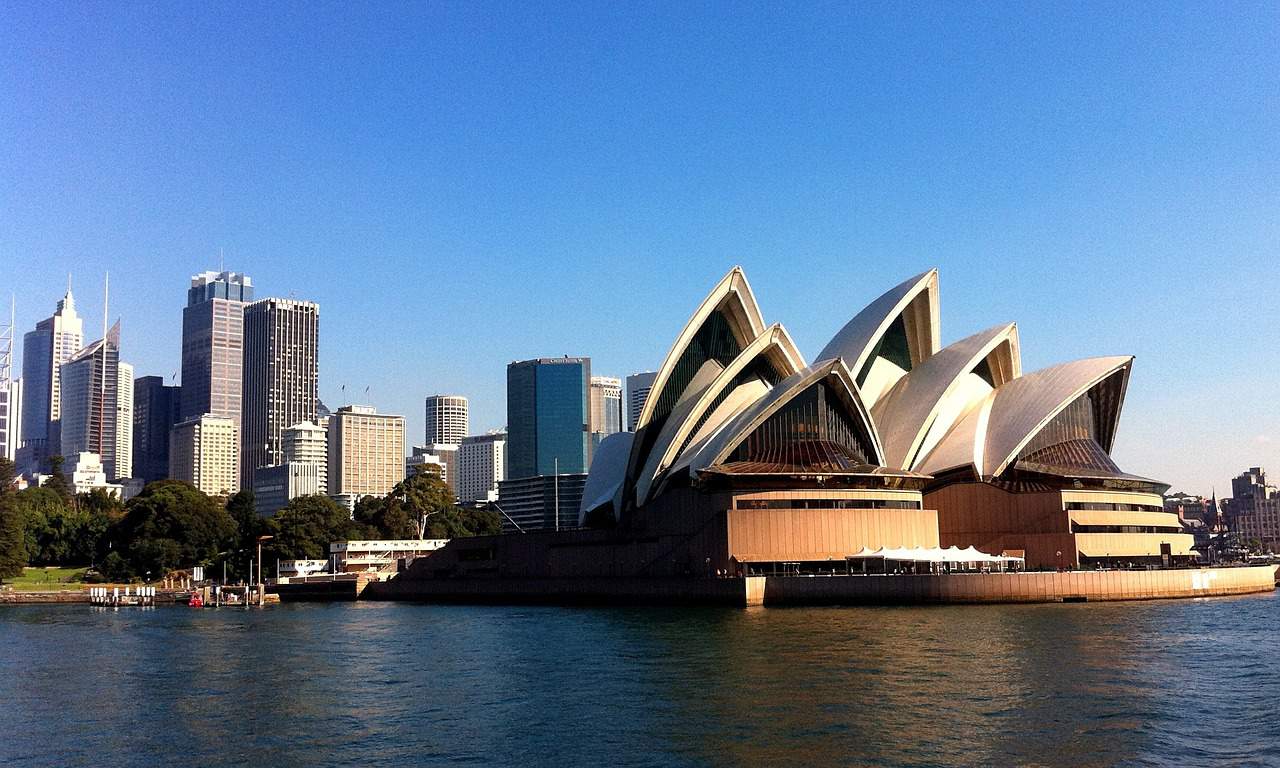
The Australian continent is almost entirely smooth and flat. That is because this is what geologists call “the old” earth. It has been worn down by millions of years of wind and rain until the hills in much of the country are gently rolling hills, something like the hills of New England.

When did Australia become a country?
Australia attained independence nation on January 1, 1901, after the British Parliament approved a law that allowed the six Australian colonies to administer the Commonwealth of Australia exclusively. During this time, the Australia Commonwealth become a constitutional monarchy. The legitimate, since the Australia Commonwealth was constituted with a composite constitution and Queen Victoria was the monarchy of the Australian head of state.
The Governor-General, The Constitution, and The Monarch
Australian Constitution has been recognized as one of the critical documents in its government history. He built the Commonwealth Government of Australia, characterized its structure, qualities, and methodologies, and characterized the rights and responsibilities of states with the Commonwealth.
This Constitution was put into action by an Act of the British Parliament, the Constitution Act of the Commonwealth of Australia. This law allowed six Australian colonies, still subject to the British administration, to form their Australian Commonwealth Government, with respect to the Constitution. The Constitution content was composed of agents of the six colonies in advance of the 1890s conventions and was received by referendum in each region.
As stated in the Constitution, the British sovereign was the Australian leader and, in this way, the Australian head of state. Their Constitution grants the officer specific supervisory forces that place them at another level of government. Since the important division between Australia and Great Britain, the pioneer can delegate an equipped governor-general to exercise the powers of the leader in his absence.
The governmental structure
The birth of Australia was called “Federation”. That is because their Constitution started a “federal” type of government. In a recognized structure, forces are isolated between their central government and some neighboring governments. In Australia, control was shared between the government and their six colonies government, with the Constitution changing their names to states.
Specific areas of the assembly have been authorized to the national government, including service, insurance, external relations, and post and media organizations. A complete overview of the Commonwealth’s impact can be found in section 51 of the Australian Constitution. The government can also affect the laws of the Australian territories.
States had legislative control over every problem within their borders, including police, recovery of offices, addresses, and accessible transportation. The drafting of the law has systematically established conditions in which the government and the states guarantee the ability to enact laws on a comparable subject.
Most of Australia’s contemporary discourses as a nation have been made in connection with political improvement. The ideas of the system based on voting and nationalism have been used to persuade people in a country controlled by an external political meeting that has fulfilled vital interests and must contradict this external control. As people joke with the nation to offer to all the inhabitants of a country, they stimulate recognition of the “great unitary sense” of the country.